Helium leak testing and robot handling of voluminous workpieces at high test pressure
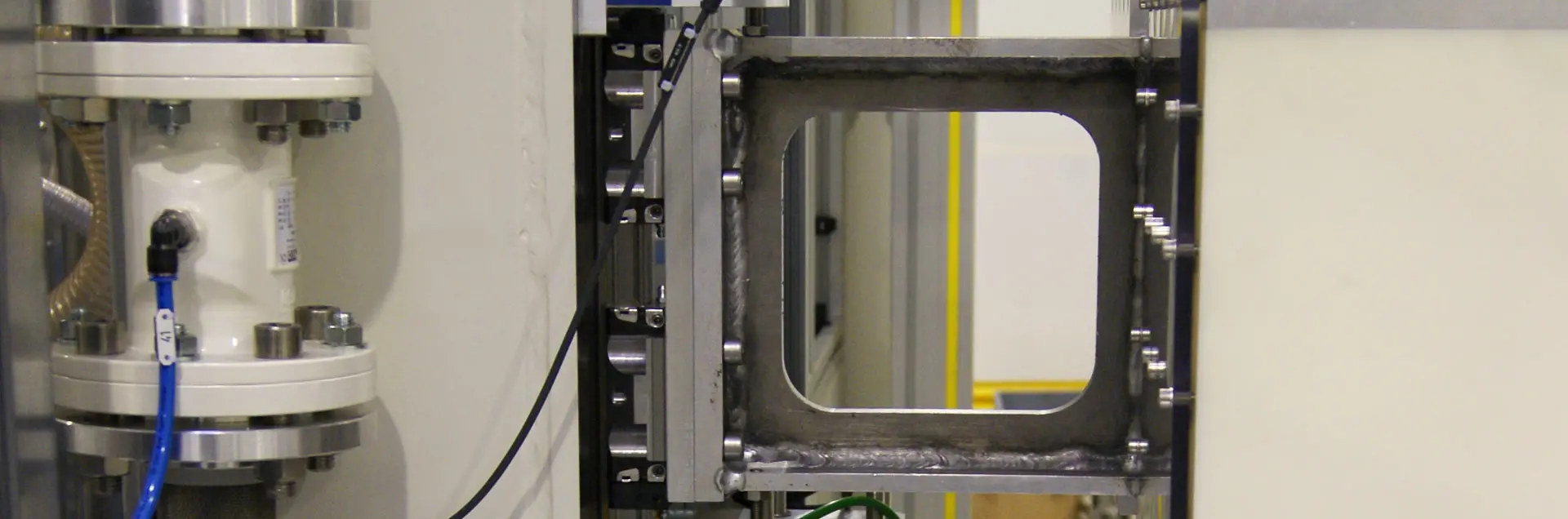
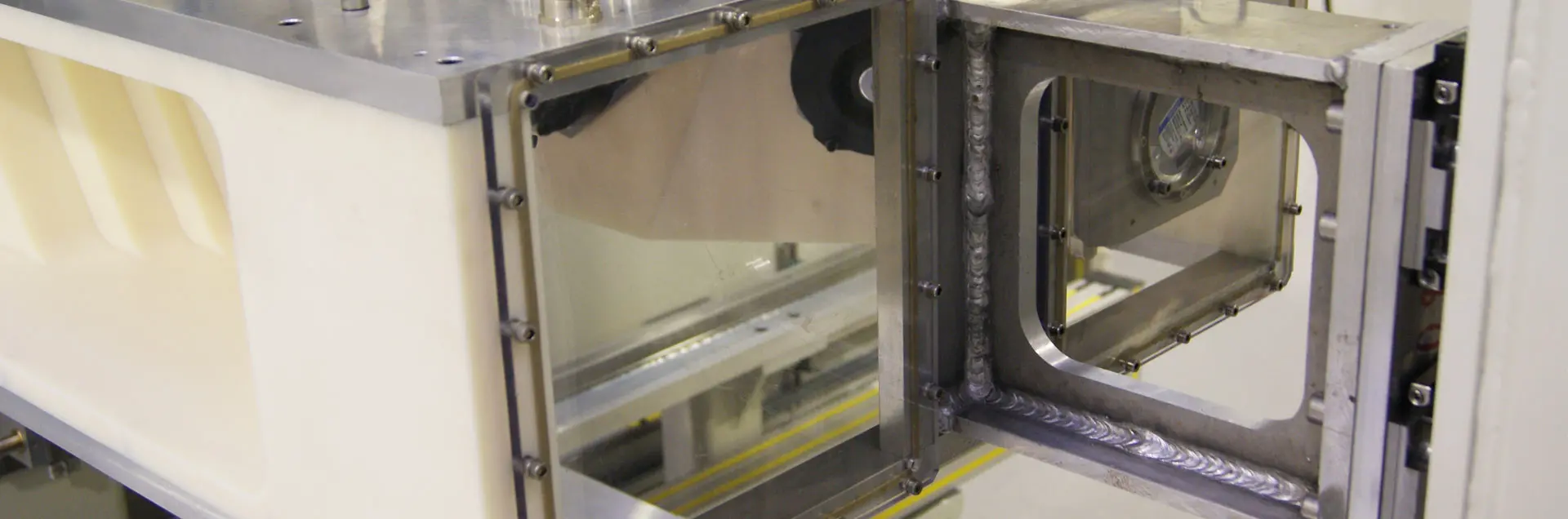
A tubular cross member is an axle beam in the body of a truck that is used as a compressed air reservoir.
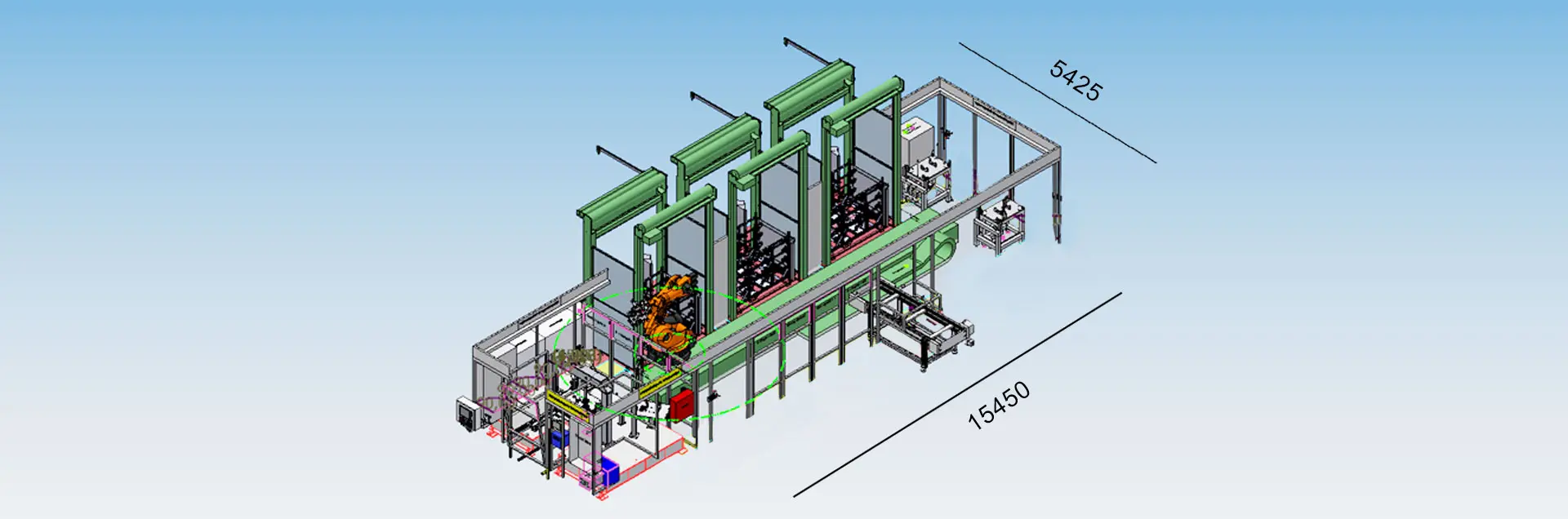
The workpieces on load carriers are loaded by the customer into staging areas, which are secured by safety roller gates. A robot on a linear axis loads and unloads the load carriers and the leak test station. The leak test station and roller door storage with robots each have their own safety circuit.
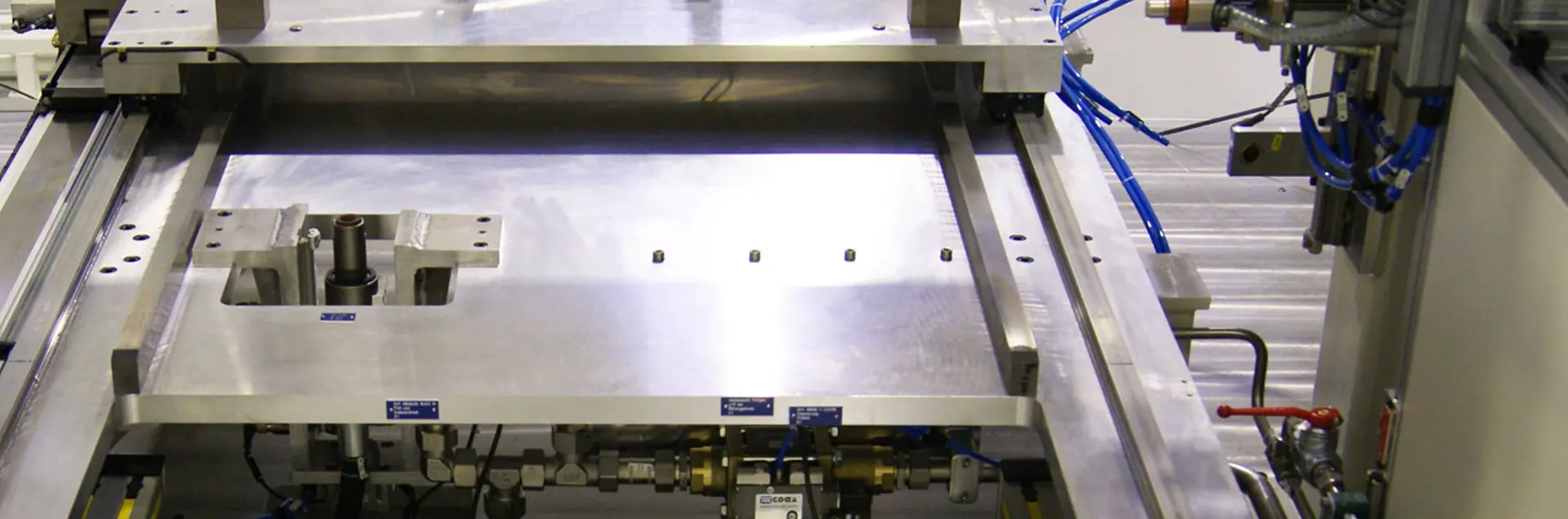
In Station 1, the robot removes the workpiece and places it in the type control station. Here a camera checks the plain text designation, reads it and saves it. Meanwhile, the robot picks up a previously leak-tested workpiece and places it in the interim storage. It then loads the type-controlled part onto the feed slide of the leak test station. The feed slide pulls the workpiece into the test position.
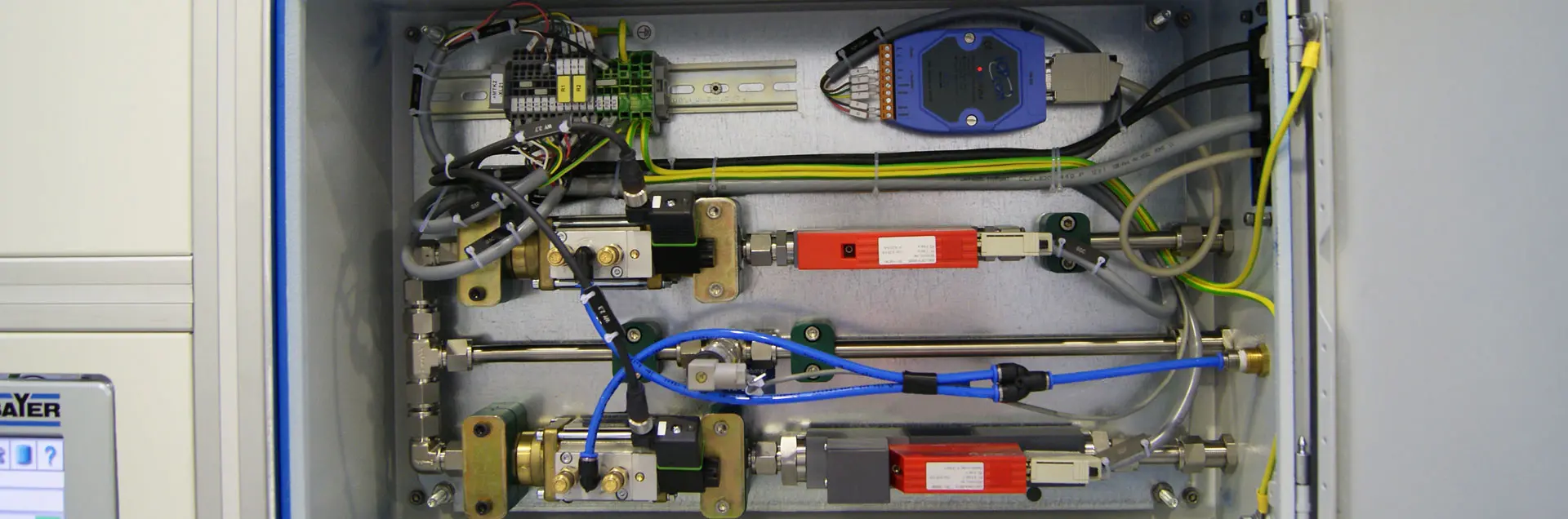
In station 2, the workpiece is clamped, sealed and passed over by a test bell and the workpiece interior is evacuated. After a coarse leak test, a gas mixer developed in-house for this application fills the interior of the workpiece with an air/helium mixture, which starts the actual leak test process. The helium concentration in the test bell is measured and checked for a possible increase.
At the end of the measurement, the air-helium mixture is exhausted and disposed of by the customer.
In station 3, the robot ejects NOK parts and places them on a belt conveyor.
There is a function for feeding in a master part on the system side. At NxNOK or after a specified number of pieces, it enables the master part to be automatically fed into the station and tested with or without a screw-in test leak. Alternatively, variable leakage rates can be set by a test leak built into the system.
- Number of workpiece types checked:7
- Workpiece transport:The workpiece on a load carrier in a staging station is loaded by robot onto the linear axis in the leak test station
- Cycle time:150 seconds cycle time for 100% OK parts including 1 calibration procedure per shift
- Helium leak testing:Coarse leak test by monitoring the pressure increase in the evacuated workpiece before filling with air/helium mixture, Helium leak test itself: Interior at 4 bar relative, leakage rate 1 cm³/min
- Test medium:Helium/air mixture, produced by gas mixer, concentration of helium selectable freely or in advance
- Other processes:Marking the OK parts
- Checked features:Type control, Leakage rate at a specified test pressure
- Emergency strategy: Feed slide with 3 positions; this enables manual loading and unloading of the workpieces